В этой статье вы узнаете:
Vein surgery in Germany supports safe, guideline-based treatment planning for varicose veins and venous reflux after duplex ultrasound assessment.
Leg pain, swelling, or bulging veins getting worse?
German vein specialists typically base vein surgery in Germany decisions on duplex ultrasound findings, CEAP stage, reflux mapping, and documented symptoms before recommending EVLA, RFA, sclerotherapy, or surgery.
Get a treatment planThe doctor or coordinator will answer within 24-48 hours.
Understanding vein problems that may need an operation
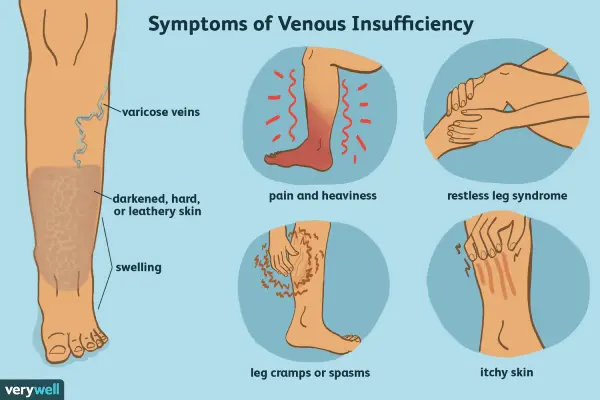
Vein surgery in Germany is most commonly performed for varicose veins and chronic venous disease. Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted surface veins, usually in the legs. They may be linked to a deeper problem called venous reflux, where valves inside the vein do not close properly and blood pools in the leg.
Many patients search for vein surgery in Germany after years of heaviness, swelling, night cramps, itching, or visible bulging veins. Clinically, German centres separate cosmetic concerns from medical disease. A procedure is usually considered when there are persistent symptoms, complications, or a clearly proven reflux pattern on ultrasound that fits the patient’s complaints.
For a broader overview of vascular care pathways, see vascular surgery in Germany.
Typical conditions assessed by German vascular and vein teams include:
- Primary varicose veins linked to reflux in the great saphenous vein or small saphenous vein
- Chronic venous insufficiency, where long-term high pressure in leg veins causes swelling, skin changes, or ulcers
- Recurrent varicose veins after prior treatment, which may need a different approach
- Venous leg ulceration that benefits from closing reflux pathways after careful evaluation
- Symptoms following deep vein thrombosis (post-thrombotic syndrome), where treatment is individualised
If there is sudden leg swelling, redness, warmth, or a new severe pain, urgent assessment is needed to exclude deep vein thrombosis. Vein surgery in Germany is not an emergency procedure, yet blood clots can be.
Diagnosis in Germany: what is checked before treatment
High-quality vein surgery in Germany starts with matching symptoms to objective findings. The key test is duplex ultrasound, which combines real-time imaging with blood flow measurements. It can show reflux, vein diameter, and the anatomical route of the problematic veins.
A vein consultation commonly includes a structured clinical exam, assessment of risk factors, and documentation of severity. Many clinics use the CEAP classification, a staging system for chronic venous disease. This helps to describe what is visible and what complications exist, and it supports consistent decision-making before vein surgery in Germany is recommended.
If you want a focused explanation of diagnostic steps patients usually need first, see duplex ultrasound diagnostics.
Useful terms that are often mentioned in reports include:
- Venous reflux: backward flow in a vein due to valve failure
- Great saphenous vein (GSV) and small saphenous vein (SSV): major surface veins that often develop reflux
- Perforator veins: connecting veins between deep and superficial systems that can contribute to disease in selected cases
- Duplex mapping: a detailed ultrasound map showing where reflux starts and where it travels
| Diagnostic step | What it shows | Why it matters for surgery selection |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical assessment | Symptoms | Links heaviness, swelling, itching, cramps, skin changes, or ulcers to the likely cause |
| Duplex ultrasound | Reflux map | Identifies reflux source and vein anatomy so vein surgery in Germany can be planned as EVLA, RFA, sclerotherapy, or surgery |
| CEAP classification | Stage | Standardises severity and supports risk discussion, follow-up planning, and documentation |
| Risk review | Safety | Considers clotting risk, infection, anticoagulants, pregnancy, and mobility needs before intervention |
Stages of venous disease and what they mean
CEAP is widely used in European practice. It does not decide treatment on its own, yet it helps clinicians communicate and compare severity. Patients usually benefit from understanding the stage because it clarifies why one method of vein surgery in Germany is recommended over another.
| CEAP clinical stage | Typical signs | Common treatment focus |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Spider veins | Often cosmetic management, lifestyle measures, selected sclerotherapy |
| C2 | Varicose veins | Ultrasound-based selection of vein surgery in Germany using EVLA, RFA, foam sclerotherapy, or surgery |
| C3 | Oedema | Compression, reflux closure when symptoms and mapping match |
| C4 | Skin changes | Medical treatment plus reflux control to reduce progression risk |
| C5–C6 | Ulcer | Wound care, compression, and carefully planned reflux management |
European guidance on chronic venous disease is discussed by professional societies such as the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): ESVS.
Vein operation methods used in Germany
Vein surgery in Germany includes minimally invasive and surgical methods, selected according to ultrasound findings, symptoms, anatomy, and prior procedures. Many treatments are performed as day procedures, with local anaesthetic or light sedation depending on complexity and clinic practice.
For an overview focused specifically on common treatment routes, see varicose veins treatment.
Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA or EVLT)
EVLA uses a thin laser fibre placed inside the vein under ultrasound guidance. Heat closes the refluxing vein from within. Over time, the body reroutes blood through healthier veins. In vein surgery in Germany, EVLA is often considered for reflux in the great or small saphenous vein, and it is frequently combined with treatment of side branches.
Patients usually ask whether “laser is better than surgery”. The most accurate answer is that outcomes depend on correct indication, technique, and follow-up. Laser can be highly effective for suitable reflux patterns, yet it is not the right choice for every anatomy. A focused explanation of laser options is available at endovenous laser therapy.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
RFA is another endovenous thermal method used in vein surgery in Germany. A catheter delivers controlled heat to close the vein. Some patients experience less post-procedure tightness compared with laser, yet both methods have strong evidence when used appropriately. Selection often depends on vein size, shape, and local expertise.
Ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy
Foam sclerotherapy injects a special foam into the vein, irritating the lining and closing the vessel. In vein surgery in Germany pathways, it can be used for certain varicose veins, residual branches after thermal treatment, or selected recurrences. It can also be an option for patients who are not ideal candidates for thermal procedures. A practical overview is available at sclerotherapy in Germany.
Miniphlebectomy and treatment of side branches
Bulging surface branches may be removed through tiny skin openings (miniphlebectomy). This is often combined with closing the main reflux source. A frequent reason for disappointment after a “quick cosmetic procedure” is that the refluxing trunk vein was never treated, allowing pressure to persist despite visible improvement.
Classical surgery: ligation and stripping
Traditional surgery includes tying off reflux sources and removing segments of the saphenous vein (stripping). It is less common than in the past because endovenous methods are widely available. Surgery can still be appropriate for certain anatomies, very large or tortuous veins, or when endovenous access is not feasible. Decisions for vein surgery in Germany are usually made after duplex mapping and a candid risk-benefit discussion.
Which method is best for a specific patient
Choosing vein surgery in Germany is usually a structured clinical decision rather than a preference for a single device. A high-quality recommendation links ultrasound findings to the symptoms and the patient’s priorities, such as return to work, prior clotting history, and tolerance for compression therapy.
These factors commonly influence selection in vein surgery in Germany:
- Where reflux starts and how far it travels
- Diameter and shape of the refluxing vein, including tortuosity
- History of prior interventions and the pattern of recurrence
- Coexisting medical issues, including mobility limitations and anticoagulant use
- Pregnancy status and timing, because treatment may be postponed in pregnancy
- Skin changes or ulcers, where comprehensive care is essential
| Method | Typical use case | Key consideration |
|---|---|---|
| EVLA | Reflux trunk | Strong option in vein surgery in Germany for mapped saphenous reflux when anatomy allows straight catheter placement |
| RFA | Reflux trunk | Thermal closure with controlled heating; selection depends on vein size and clinic protocol |
| Foam sclerotherapy | Branches | Useful for side branches or selected cases; recurrence risk should be discussed and followed |
| Miniphlebectomy | Bulging veins | Targets visible branches; best results when reflux source is treated as well |
| Stripping surgery | Complex anatomy | Option for tortuous or very large veins, or when endovenous access is unsuitable |
Who should consider vein surgery and who should not
A “candidate” is someone whose symptoms and ultrasound findings suggest that closing reflux will likely reduce venous pressure and improve function. Vein surgery in Germany is commonly recommended when symptoms are persistent and clearly linked to reflux on duplex ultrasound.
Typical indications
- Symptomatic varicose veins with proven reflux on duplex ultrasound
- Persistent swelling linked to venous insufficiency after clinical assessment
- Skin changes caused by venous hypertension, including eczema or lipodermatosclerosis
- Recurrent superficial thrombophlebitis related to varicose veins
- Venous ulcer or healed ulcer where reflux closure is part of a wider care plan
Common reasons to postpone or avoid a procedure
- Acute deep vein thrombosis or suspected pulmonary embolism, which needs urgent medical care
- Untreated infection in the area to be treated
- Pregnancy, where management is usually conservative until after delivery
- Severe arterial disease in the leg, where compression and interventions require specialist planning
- Inability to walk after the procedure, because mobility helps reduce clot risk
Risks and possible complications
Vein surgery in Germany is planned with safety checks, yet no procedure is risk-free. In experienced hands, complications are usually uncommon, yet patients benefit from knowing what to watch for and what is normal. The exact risk profile depends on the method, personal health factors, and adherence to aftercare.
Possible risks include:
- Bruising, tenderness, and tightness along the treated vein
- Skin irritation or inflammation after sclerotherapy
- Nerve irritation causing temporary numbness, more likely near the ankle with certain techniques
- Superficial thrombophlebitis, an inflammation of treated superficial veins
- Deep vein thrombosis, which is rare yet important to prevent through risk assessment and early walking
- Skin burns, pigmentation, or small wounds, uncommon with proper technique and monitoring
For plain-language background on varicose vein complications and general treatment principles, see: Mayo Clinic.
Recovery and what patients usually experience
Recovery after vein surgery in Germany depends on the method and how extensive treatment is. Many minimally invasive procedures are day-case treatments, and many patients walk immediately afterwards. Clinics often recommend compression for a defined period, and a follow-up ultrasound may be arranged to confirm closure and exclude complications.
Typical recovery milestones
- Same day: walking is encouraged, with guidance on pain relief and compression use
- 2–7 days: bruising and tightness can peak, especially after thermal ablation or phlebectomy
- 7–14 days: many patients resume routine work, depending on job type and discomfort
- 4–6 weeks: appearance improves and most tenderness resolves, with ongoing benefits for symptoms
Patients with long flights, high clot risk, or complex venous disease may need individualised advice. This is why vein surgery in Germany typically includes a structured risk review covering medication and mobility.
Cost of vein operations in Germany
Costs for vein surgery in Germany vary based on the method, the number of veins treated, clinic setting, anaesthesia, and whether treatment is staged. The most accurate estimate comes after reviewing duplex ultrasound results and clarifying the clinical objective, such as symptom control, ulcer prevention, or management of recurrence.
The figures below are typical self-pay ranges used for orientation. They are not a guarantee and may change after medical review. For general cost planning, see cost of treatment in Germany.
| Treatment type | Typical setting | Estimated cost range (€) |
|---|---|---|
| Duplex ultrasound consultation | Outpatient | 120–350 |
| EVLA (1 leg, mapped reflux trunk) | Day case | 1800–3500 |
| RFA (1 leg, mapped reflux trunk) | Day case | 2000–3800 |
| Foam sclerotherapy session | Outpatient | 250–900 |
| Miniphlebectomy (branches) | Day case | 900–2200 |
| Stripping surgery (complex cases) | Surgery | 2500–6500 |
| Follow-up ultrasound | Outpatient | 80–250 |
Common patient mistakes that reduce results
Disappointing outcomes after vein surgery in Germany are often linked to mismatched expectations or incomplete assessment rather than a single “wrong technique”. The following issues are frequently seen in clinical practice:
- Treating visible veins without mapping and closing the reflux source
- Assuming all leg pain is caused by varicose veins, when back, hip, arterial, or nerve causes exist
- Skipping compression advice when it is recommended for a defined period
- Returning to high-impact activity too quickly after extensive phlebectomy
- Not attending a follow-up ultrasound, where early issues can be detected and managed
Evidence summaries and clinical background on chronic venous disease are available through: NCBI and PubMed.
Real clinical situations: how treatment choice can differ
Scenario 1: Bulging veins with heaviness after standing
Duplex ultrasound shows reflux in the great saphenous vein. A German clinic may recommend vein surgery in Germany using EVLA or RFA to close the reflux trunk and add miniphlebectomy for prominent branches. The aim is symptom reduction and prevention of progression, while keeping recovery relatively quick.
Scenario 2: Recurrent varicose veins after prior stripping
Ultrasound mapping identifies new reflux routes or residual stump reflux. Treatment may be more targeted and can include foam sclerotherapy, endovenous ablation if anatomy allows, or selective surgery. A careful plan matters because recurrent disease can have complex anatomy, and vein surgery in Germany is often tailored to that mapping.
Scenario 3: Skin changes and a history of a healed venous ulcer
Management often includes compression, skin care, and reflux closure when a clear reflux source is documented. The aim is to reduce venous pressure that contributes to skin damage. A realistic discussion includes long-term prevention and the need for ongoing care, even after vein surgery in Germany.
Why many patients choose Germany for vein surgery
Vein surgery in Germany is frequently chosen for structured diagnostics, consistent documentation, and wide availability of modern endovenous techniques. Many centres follow guideline-based pathways, use duplex ultrasound mapping as a core standard, and prioritise safe patient selection before intervention.
Practical advantages can include:
- Access to vascular surgeons and phlebology-focused teams with high procedure volumes
- Clear imaging-based decision-making, with written findings and structured staging
- Availability of multiple techniques, allowing selection based on anatomy rather than a single device
- Follow-up protocols that include ultrasound checks where clinically appropriate
More context on choosing Germany for treatment is available at treatment in Germany.
How Kliniki.de supports your medical decision
Kliniki.de helps patients request a medical treatment plan built on documented findings. A useful plan for vein surgery in Germany typically starts with duplex ultrasound results, CEAP stage, symptom history, and relevant medical risks such as anticoagulant therapy or prior thrombosis.
If you already have documents, sending them for review can reduce uncertainty and help avoid unnecessary procedures. Helpful documents include ultrasound reports, prior operation notes, medication lists, and photos of visible skin changes when relevant. For process details, see how Kliniki.de works.
Still unsure which vein surgery in Germany fits your ultrasound?
Send duplex ultrasound findings, CEAP stage, symptom history, and medication list for a doctor-led review that can clarify indications, options, expected recovery, and a realistic cost estimate.
Get a treatment planThe doctor or coordinator will answer within 24-48 hours.

