В этой статье вы узнаете:
Implantable Loop Recorder in Cardiology (ILR): A Innovative Monitoring Solution
An implantable loop recorder (ILR) is a small, thin device that is implanted under the skin in your chest. It is used to continuously record your heart rhythm for up to three years. ILRs are used to diagnose and monitor a variety of heart conditions, including:
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Heart palpitations
- Syncope (fainting)
How is an ILR implanted?
The ILR is implanted under the skin in your chest, just below your collarbone. The procedure is usually done under local anesthesia, and it takes about 30 minutes.
How does an ILR work?
The ILR continuously records your heart rhythm and stores the data on a memory chip. The data can be downloaded to a computer and analyzed by a doctor.
ILR Procedure: A Deep Dive
The implantable loop recorder (ILR) procedure is a minimally invasive technique used to diagnose and monitor irregular heart rhythms. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the procedure:
Preparation:
- Pre-operative assessment: Your doctor will assess your medical history, perform physical exams, and potentially conduct additional tests like EKGs or blood work.
- Informed consent: You will receive detailed information about the procedure, its risks and benefits, and alternative options. Signing an informed consent form is mandatory.
- Medications: Certain medications may need to be adjusted or stopped before the procedure.
The Procedure:
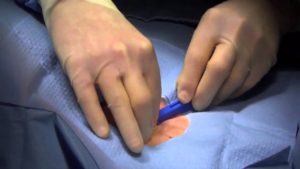
- Local anesthesia: The area around the incision site is numbed, while you remain awake and relaxed.
- Incision: A small incision (3-4 cm) is made just below your left collarbone.
- Device insertion: The ILR, a small, thin device, is inserted into a pocket created under the skin.
- Connection: The ILR’s leads are connected to the heart tissue to monitor its electrical activity.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or surgical glue.
- Recovery: You will be monitored for a short period before being discharged, usually the same day.
Post-Procedure:
- Activity restriction: Avoid strenuous activities for a few days.
- Wound care: Keep the incision site clean and dry.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor the ILR’s function and analyze recorded data.
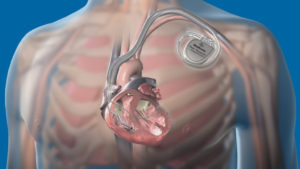
How Implantable Loop Recorders (ILRs) Record: A Technical Insight
Implantable loop recorders (ILRs) are small, sophisticated devices that continuously monitor and record your heart rhythm for up to three years. These devices offer a valuable diagnostic tool for cardiologists, providing critical information about cardiac events and helping to identify and manage arrhythmias.
At the core of ILR functionality lies its recording mechanism:
1. Continuous Looping:
- ILRs operate on a “looping” principle, continuously recording and overwriting data in a circular buffer.
- The buffer typically stores several minutes of heart rhythm data, ensuring that even brief arrhythmic events are captured.
- New data continuously overwrites older data, allowing for long-term monitoring without the need for large memory storage.
2. Event Triggered Recording:
- In addition to continuous recording, ILRs can be configured to automatically detect and record specific cardiac events.
- This event-triggered recording is based on various criteria, such as:
- Heart rate exceeding a certain threshold (e.g., too high or too low)
- Abnormal heart rhythms (e.g., bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation)
- Patient-activated recording using a handheld device
3. Data Storage and Transmission:
- Recorded data is stored on the ILR’s internal memory chip.
- Data can be periodically transmitted wirelessly to a transmitter device worn by the patient.
- The transmitter then sends the data over a cellular network to a secure server for analysis by cardiologists.
4. Advanced Features:
- Some ILRs offer additional features, such as:
- Subclinical atrial fibrillation (AFib) detection: Detects AFib episodes that may not cause symptoms, aiding in early diagnosis and treatment.
- Heart rate variability (HRV) analysis: Provides insights into the autonomic nervous system’s influence on heart rate, helping to assess cardiac health and risk of arrhythmias.
By combining continuous monitoring, event-triggered recording, and advanced data analysis, ILRs provide a comprehensive and accurate picture of your heart rhythm, helping to diagnose and manage arrhythmias effectively.
It’s important to note that ILR technology continues to evolve, with newer models incorporating advancements in miniaturization, data storage, and wireless communication.
Who is an Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR) indicated for?
An implantable loop recorder (ILR) is a small device that is implanted under the skin of your chest to continuously record your heart rhythm for up to 3 years. ILRs can be indicated for people with:
1. Unexplained symptoms:
- Paroxysmal tachycardia: fast heart rate
- Paroxysmal bradycardia: slow heart rate
- Palpitations: feeling of skipped or irregular heartbeats
- Fainting or near-fainting spells
- Syncopal episodes
2. Suspected arrhythmia:
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib)
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
- WPW syndrome
- Long QT syndrome
- Arrhythmia after heart surgery
3. Risk factors for arrhythmia:
- Heart failure
- Coronary artery disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Older age
- Family history of arrhythmia
4. Need to monitor the effectiveness of treatment:
- Antiarrhythmic therapy
- Ablation
- Pacemaker or defibrillator implantation
The decision to recommend an ILR is made by a doctor based on:
- Medical history
- Results of ECG, Holter monitoring, echocardiography
- Risk-benefit assessment
ILRs are not recommended for:
- Pregnant women
- People with infections
- People with allergies to ILR materials
- People with severe psychiatric disorders
Benefits of ILRs in Cardiology: A Powerful Tool for Diagnosis and Management
Implantable loop recorders (ILRs) have become invaluable tools in the field of cardiology, offering a unique set of advantages over traditional methods for monitoring heart rhythm. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy:
- Continuous monitoring: Unlike EKGs, ILRs capture heart rhythm 24/7, significantly increasing the chance of capturing infrequent or fleeting arrhythmias that might be missed by other methods.
- Long-term data collection: Extended monitoring periods (up to 3 years) allow for a more comprehensive understanding of arrhythmia patterns and their triggers.
- Detailed information: ILRs record additional data beyond rhythm, such as heart rate variability, providing valuable insights into heart function and autonomic nervous system activity.
Improved Patient Management:
- Targeted treatment: Accurate diagnosis leads to more precise and effective treatment strategies for arrhythmias.
- Reduced medication use: By pinpointing the exact cause of symptoms, unnecessary medications can be avoided, potentially reducing side effects and improving quality of life.
- Risk stratification: Identifying individuals at high risk for future arrhythmias allows for preventative measures and early intervention.
- Peace of mind: Knowing their heart rhythm is being monitored can provide significant reassurance and reduce anxiety for patients with a history of arrhythmias.
Additional Advantages:
- Minimally invasive procedure: Implantation is a quick, outpatient procedure with minimal discomfort and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- Discreet and comfortable: The compact size and subdermal placement make the ILR virtually undetectable and unobtrusive in daily life.
- Data accessibility: Recorded data can be easily downloaded and analyzed by doctors remotely, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
However, it’s important to consider:
- Not suitable for everyone: Specific patient needs and medical conditions might not be compatible with ILR implantation.
- Potential risks: While rare, risks like infection, bleeding, or device malfunction exist.
- Cost: The procedure and device itself can be costly, although insurance coverage may be available.
Overall, ILRs offer a valuable combination of diagnostic accuracy, improved patient management, and convenience, making them a powerful tool for cardiologists to manage and improve the lives of patients with arrhythmias.


